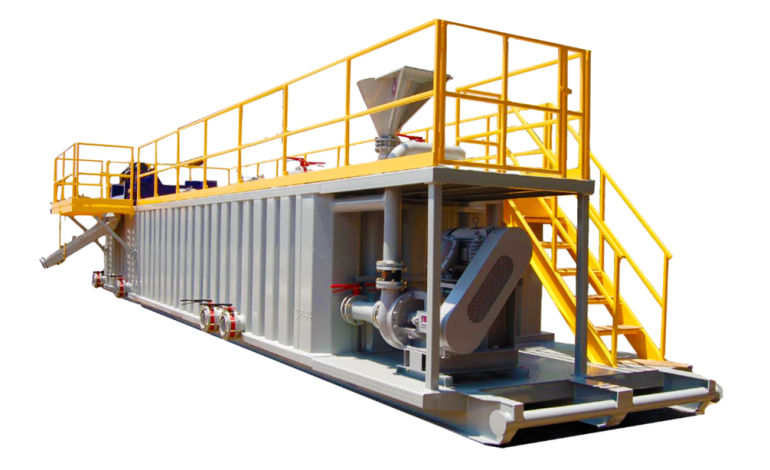

Mud tank is a commonly used equipment in oil drilling, geological exploration and other fields.
Its main function includes storing and handling drilling mud. The mud tank is usually made of strong metal material with a certain capacity and strength to withstand the weight and pressure of the mud. Structurally, it is generally equipped with a mixing device to maintain the uniformity and stability of the mud; inlet and outlet piping for mud injection and discharge; a level monitoring device to keep abreast of the amount of mud in the tank; and a filtration and purification system to remove impurities and unwanted components from the mud. The design and specifications of mud tanks will vary according to specific application scenarios and needs. For example, in deep well drilling, a larger capacity and more sophisticated features may be required. Maintenance of the mud tank is also very important, and regular checks of the integrity of the tank, the operation of the mixing unit, and the sealing of the pipework are required to ensure that it is working properly and that drilling operations are carried out safely and efficiently.
The working principle of mud tank mainly includes the following steps:
- Mud storage: Mud flows out of the wellhead during drilling and enters the mud circulation tank through the mud inlet and outlet. Inside the tank, the mixing system keeps the mud uniform and prevents the mud from settling and solidifying.
- Mud purification: Mud purification equipment removes impurities and solid-phase particles from the mud and improves the quality of the mud. These equipment may include vibrating screens, desanders, mud removers, etc.
- Circulating mud: the purified mud is re-delivered to the drilling wellhead through mud pumps to achieve mud recycling. This reduces mud wastage and maintains the mud properties required for the drilling process.
- Maintaining pressure balance: The mud circulation tank plays an important role in storing, mixing, purifying and circulating mud during the drilling process. As an important part of the surface fluid treatment system of drilling equipment, it not only provides sufficient treated drilling fluid for drilling construction, but also plays an important role in maintaining the pressure balance of the wellhead, cooling the drill bit and transporting rock chips.
In actual application, the working principle of mud tank may vary depending on the specific equipment and process. At the same time, in order to ensure the normal operation of the mud tank, it is also necessary to carry out regular maintenance and repair.
Mud tank has several significant advantages as follows:
- Efficient storage: able to hold a large amount of mud to meet the continuous demand during drilling operations, reducing the frequency of mud replenishment and improving operational efficiency.
- Stable performance: with good structural strength and stability, it can withstand the weight and pressure of mud, and ensure that it is not easy to be deformed or damaged under adverse working conditions.
- Purification: Equipped with effective purification equipment, it can remove impurities and solid-phase particles in the slurry and improve the quality of the slurry, thus prolonging the service life of the slurry and reducing the cost.
- Accurate control: Equipped with liquid level monitoring and control system, it can accurately grasp the stock of slurry, which is convenient for timely adjustment and management of the use of slurry.
- Uniform mixing: The internal mixing device can keep the slurry with uniform composition and performance, prevent the slurry from stratification or precipitation, and ensure its consistency in use.
- Safety and security: It can effectively control the mud flow and pressure, which helps to maintain the pressure balance at the wellhead and reduce the risk of drilling accidents.
- Convenient for maintenance: the structure is relatively simple and easy to carry out daily inspection, repair and maintenance, which reduces the maintenance cost and downtime of the equipment.
- Flexible and mobile: some mud tanks are designed to be mobile, which is convenient for flexible deployment and use between different drilling sites.
- Environmental protection and energy saving: by recycling mud, it reduces the waste of mud and pollution to the environment, and also reduces energy consumption.
- Adaptable to various working conditions: it can be customised and adjusted according to different drilling conditions and requirements, with strong adaptability.
When using a slurry tank, these following precautions need to be kept in mind:
- solid installation: ensure that the slurry tank is installed on a level, solid foundation to prevent the tank from tilting or shifting, which could affect normal operation and safety.
- regular inspection: including the structural integrity of the tank, check whether there are cracks, corrosion or deformation; whether the pipeline connections are tight and there is no leakage; whether the mixing device is functioning properly, etc.
- Cleaning and maintenance: Regularly clean the sediments and impurities inside the tank to prevent clogging the pipeline and affecting the performance of the slurry. Meanwhile, keep the outside of the tank clean to prolong the service life.
- Operation specification: the operator should be familiar with the operation regulations of the mud tank, and carry out the operation of mud injection, discharge and mixing in accordance with the stipulated process.
- safety protection: set up necessary protection facilities, such as guardrails, warning signs, etc., to prevent people from accidentally falling or coming into contact with the equipment in operation.
- Electrical safety: If the slurry tank is equipped with electrical equipment, make sure the electrical system is well grounded to avoid leakage and electric shock.
- Temperature control: In some cases, it is necessary to pay attention to the temperature of the slurry to avoid excessive high or low temperatures that may adversely affect the performance of the slurry.
- Pressure monitoring: closely monitor the pressure in the tank to ensure that it is within safe limits and to prevent overpressure from causing tank rupture.
- Emergency Preparation: Formulate an emergency plan and equip necessary emergency equipment and materials to cope with possible leaks, failures and other emergencies.
- training and education: conduct regular training and safety education for operators to improve their safety awareness and operation skills.

There are several key factors to consider when choosing the right mud tank:
- Operational requirements: Firstly, it is important to define the size, depth and duration of the drilling or engineering operation, as well as the volume of mud to be handled. Larger, deeper drilling wells usually require larger capacity mud tanks.
- Mud characteristics: Consider the composition, density, viscosity and other characteristics of the mud to determine whether the tank can adapt to and effectively handle this type of mud.
- Material quality: High quality materials such as high strength steel can provide better durability and corrosion resistance to ensure long term use.
- Functional configuration: such as the efficiency and power of the mixing device, the performance and accuracy of the filtration and purification equipment, etc., to meet the requirements of the operation on the slurry processing.
- Size and shape: according to the space size of the operation site, choose the appropriate size and shape of the slurry tank to ensure the convenience of installation and use.
- Pressure tolerance: According to the pressure situation that may occur in the operation, choose the slurry tank that can withstand the corresponding pressure to ensure safe operation.
- Mobility needs: If you need to move frequently in different sites, you can choose a portable slurry tank that is easy to transport and install.
- Brand name and reputation: choose a manufacturer with good reputation and rich experience, its product quality and after-sales service is usually more guaranteed.
- budget constraints: under the premise of meeting the operational needs, combined with the budget to choose a cost-effective mud tank.
- After-sales service: understand the after-sales service provided by the manufacturer or supplier, including repair, maintenance, spare parts supply, etc., to ensure the long-term stable operation of the equipment.
Comprehensive consideration of the above factors can help you choose the most suitable slurry tank for specific application scenarios.
The daily maintenance points of the mud tank include the following aspects:
- Regular cleaning: Remove mud residues, sediments and impurities from the tank to avoid blocking the pipeline and affecting the quality of the mud. At the same time, clean the outside of the tank to prevent corrosion.
- check the tank: carefully check the tank for corrosion, cracks, deformation, etc., to ensure that the tank structure is intact and solid.
- Pipeline maintenance: check the pipeline in and out of the slurry for wear and tear, leakage and blockage, and replace the damaged pipeline or pipe fittings in time.
- mixing device: check the wear and tear of mixing shaft and blades, and ensure that the mixing device operates normally and is well lubricated.
- Filtration system: clean or replace the filter mesh and filter element of the filtration equipment to ensure the filtration effect.
- Instrument calibration: calibrate the liquid level meter, pressure gauge and other instruments regularly to ensure accurate measurement.
- Valve maintenance: switch operation of valves, check their flexibility, apply lubricant to prevent jamming, and replace them in time if damaged.
- electrical system: check whether the electrical connection is loose, whether the wires are broken, to ensure the normal operation of electrical equipment.
- anti-corrosion treatment: check and repair the anti-corrosion coating on the surface of the tank to prevent rust and corrosion.
- Fastening of parts: Regularly check the fastening of all connecting parts, such as bolts and nuts, to prevent loosening.
- Record maintenance: Make a good record of maintenance, including maintenance time, content, problems found and treatment methods.
- Training operation: Strengthen the training of operators to make them familiar with the correct operation and maintenance procedures.


